
Types of acquisitions Static acquisitions and live acquisitions Four methods Bit-stream disk-to-image file Bit-stream disk-to-disk Logical disk-to-disk or disk-to-disk data Sparse data copy of a file or folder Guide to Computer Forensics and Investigationsġ1 Determining the Best Acquisition Method (continued)īit-stream disk-to-image file Most common method Can make more than one copy Copies are bit-for-bit replications of the original drive ProDiscover, EnCase, FTK, SMART, Sleuth Kit, X-Ways, iLook Bit-stream disk-to-disk When disk-to-image copy is not possible Consider disk’s geometry configuration EnCase, SafeBack, SnapCopy Guide to Computer Forensics and Investigationsġ2 Determining the Best Acquisition Method (continued) afm for AFF metadata AFF is open source Expected standard in the future Guide to Computer Forensics and Investigationsġ0 Determining the Best Acquisition Method Garfinkel of Basis Technology Corporation Design goals Provide compressed or uncompressed image files No size restriction for disk-to-image files Provide space in the image file or segmented files for metadata Simple design with extensibility Open source for multiple platforms and OSs Guide to Computer Forensics and Investigationsĭesign goals (continued) Internal consistency checks for self-authentication File extensions include. IDIF, IRBF, IEIF formats Expert Witness format – unofficial standard Encase Guidance Software. Proprietary Formats Features offered Option to compress or not compress image files Can split an image into smaller segmented files Can integrate metadata into the image file Disadvantages Inability to share an image between different tools File size limitation for each segmented volume Guide to Computer Forensics and Investigationsħ Proprietary Formats ILook (Law enforcement agencies)

Raw Format Makes it possible to write bit-stream data to files Advantages Fast data transfers Can ignore minor data read errors on source drive Most computer forensics tools can read raw format Disadvantages Requires as much storage as original disk or data Tools might not collect marginal (bad) sectors Guide to Computer Forensics and InvestigationsĦ Guide to Computer Forensics and Investigations Three formats Raw format Proprietary formats Advanced Forensics Format (AFF) Guide to Computer Forensics and Investigationsĥ Guide to Computer Forensics and Investigations
#Making a contingency table program r studio how to#
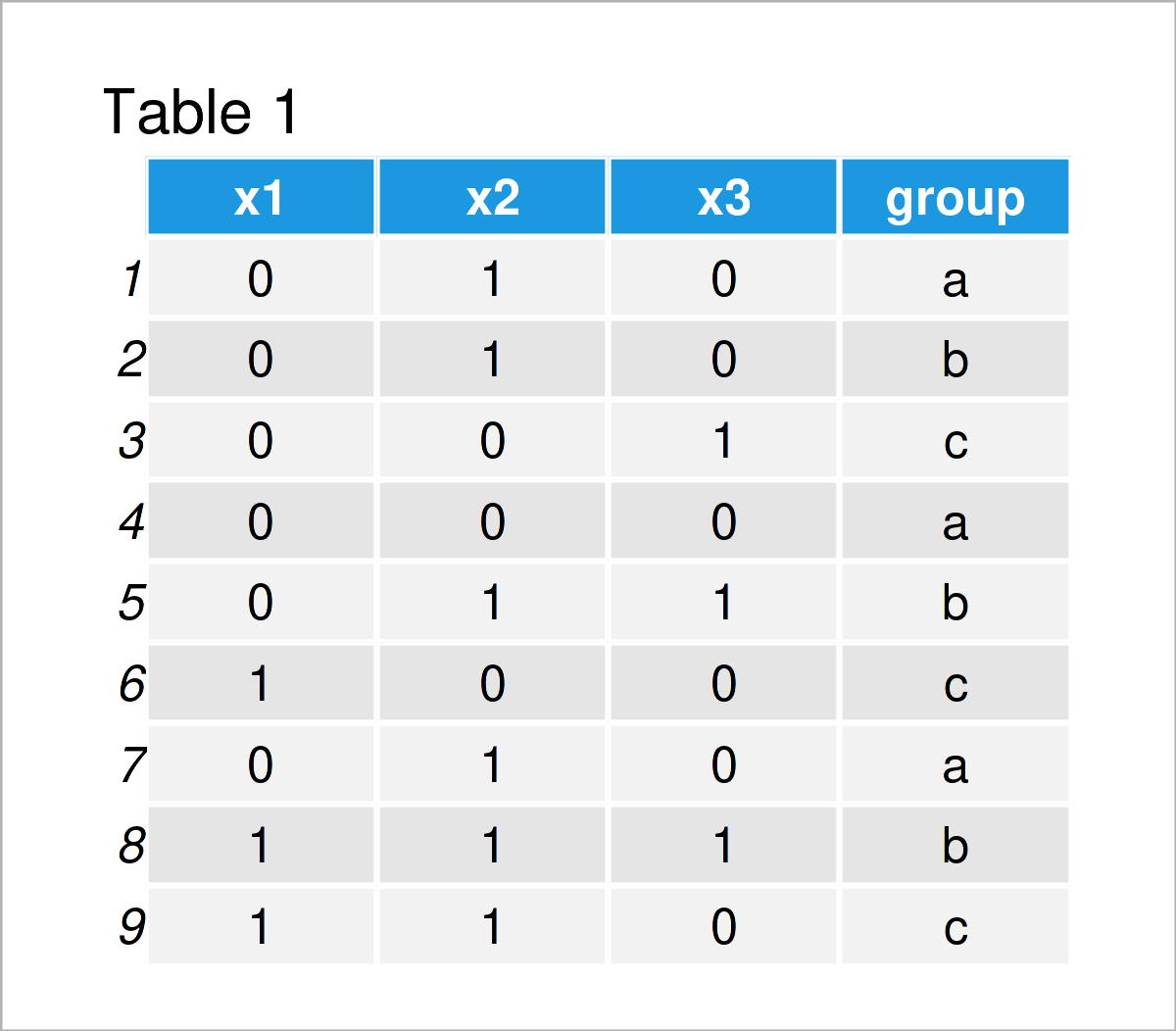
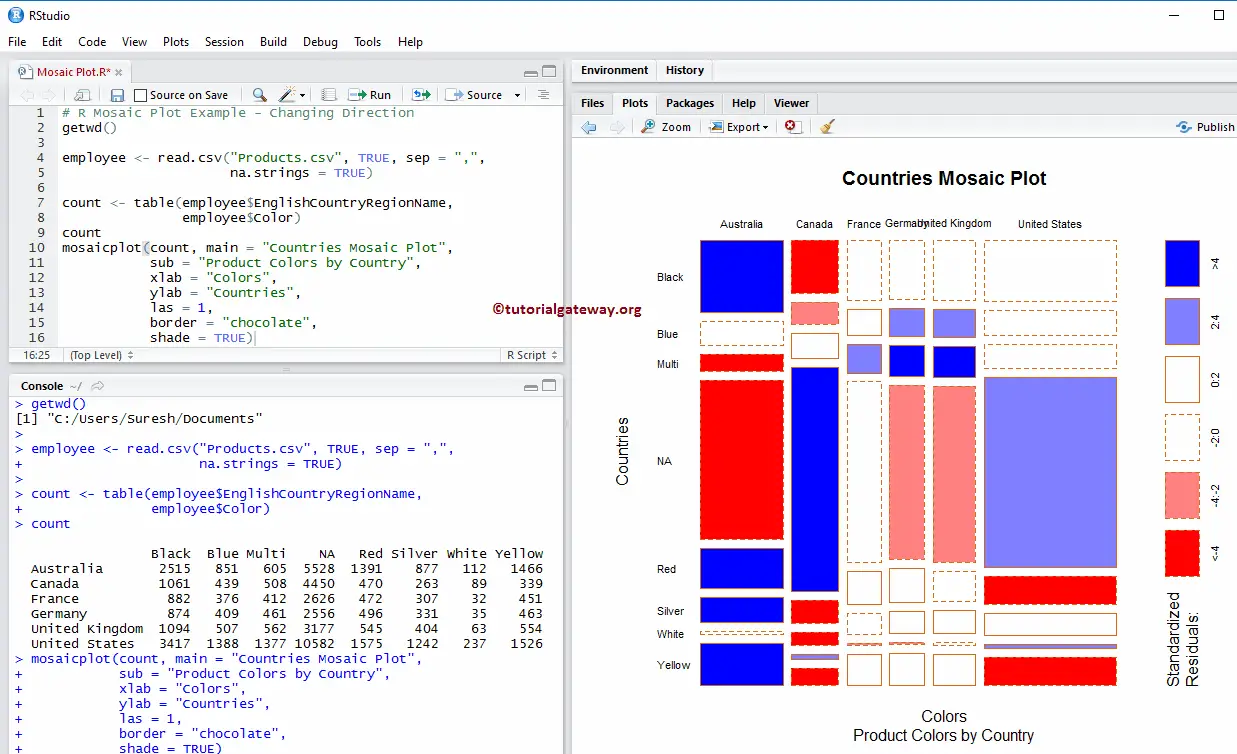
Objectives List digital evidence storage formats Explain ways to determine the best acquisition method Describe contingency planning for data acquisitions Explain how to use acquisition tools Guide to Computer Forensics and InvestigationsĮxplain how to validate data acquisitions Describe RAID acquisition methods Explain how to use remote network acquisition tools List other forensic tools available for data acquisitions Guide to Computer Forensics and InvestigationsĤ Understanding Storage Formats for Digital Evidence Let’s consider the UCBAdmisssions data set.Presentation on theme: "Guide to Computer Forensics and Investigations Third Edition"- Presentation transcript:ġ Guide to Computer Forensics and Investigations Third EditionĢ Guide to Computer Forensics and Investigations In this tutorial, let’s see how to create a mosaic plot in R Concept behind the mosaic plot: Mosaic plot is a graphical representation of two way contingency table which pictographically represents the relationship among two or more categorical variables.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
